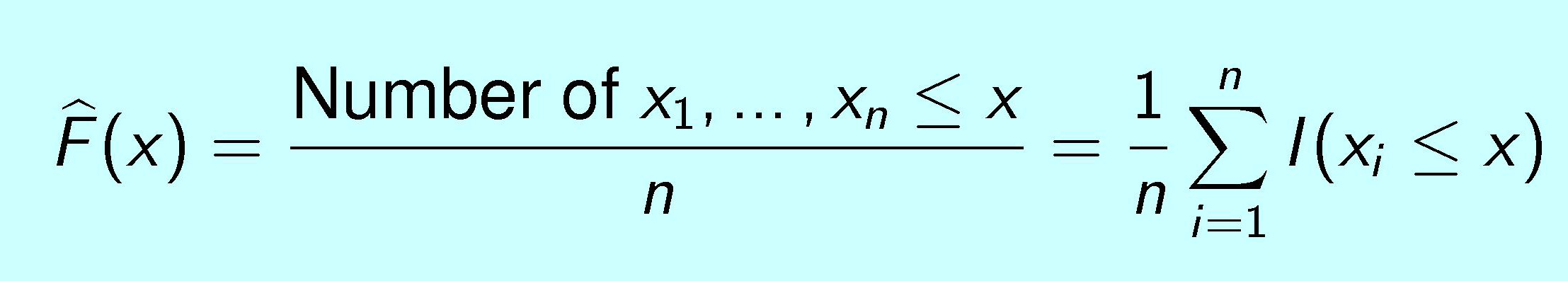|
The Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test
The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test is a significance test for comparing samples with specified probability distributions, or with each other. It has the following derivation and components:
The Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF): Any probability distribution function can be specified via its cumulative distribution function, typically denoted by F and defined for random quantity X by
That is, for any number x, F(x) computes the probability that the random quantity takes a value less than or equal to x. For example, if X records the shortest inter-object distance between objects in an image, then, say, F(2.54) defines the probability that the shortest distance is less than or equal to 2.54 units. Clearly the function F has to take values between 0 and 1, and must be non-decreasing (that is, F(a) ≤ F(b) if a < b)
The Empirical Distribution
Function (EDF): The EDF is a data-based estimate of CDF. The EDF
is denoted
where I is the indicator function: I(A)=1 if the
event A occurs, and I(A)=0 otherwise (so that
I(xi ≤ x) = 1 if xi ≤ x).
So, the hypothetical data distribution is described by F,
whereas the sample is described by
The Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test compares either
|